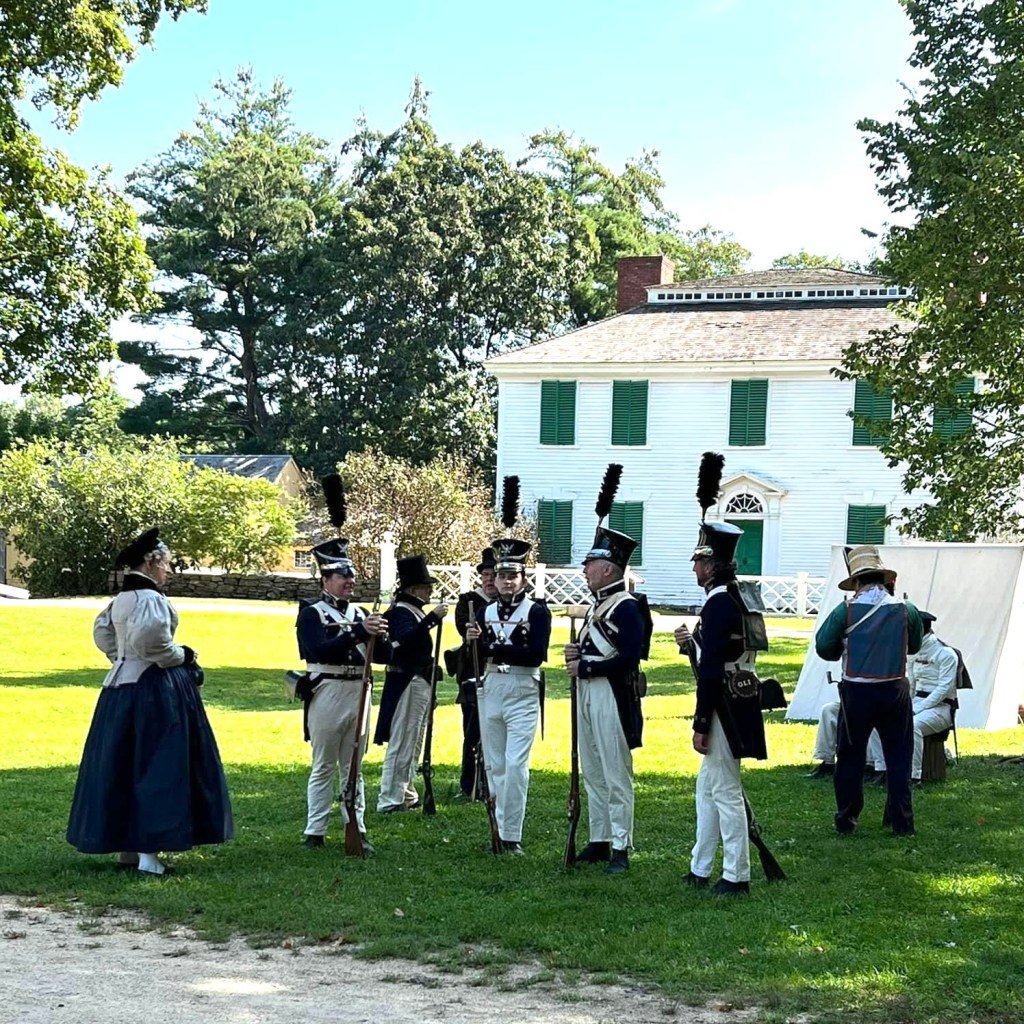
The Marquis came back (or his analog did, at least) last October 7, and we were there.
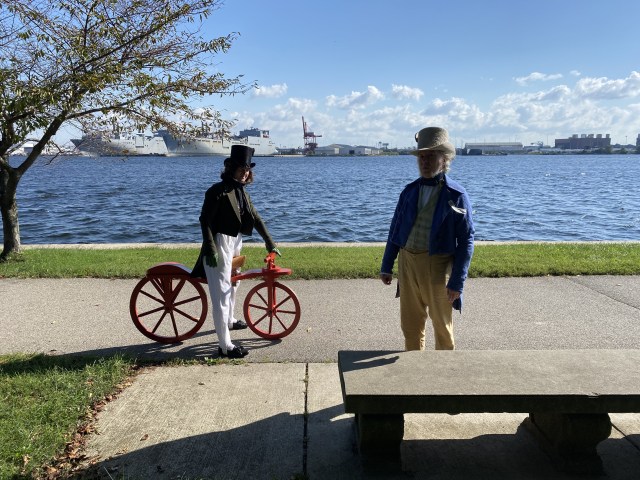

Way back in January 2024, Mr. K and I were asked by the Museum of the American Revolution if we would be interested in joining them (and their tents) at Fort McHenry to celebrate the Lafayette Centennial in Baltimore at Fort McHenry. Of course, I said yes, figuring that 10 months or so was ample time to prepare.
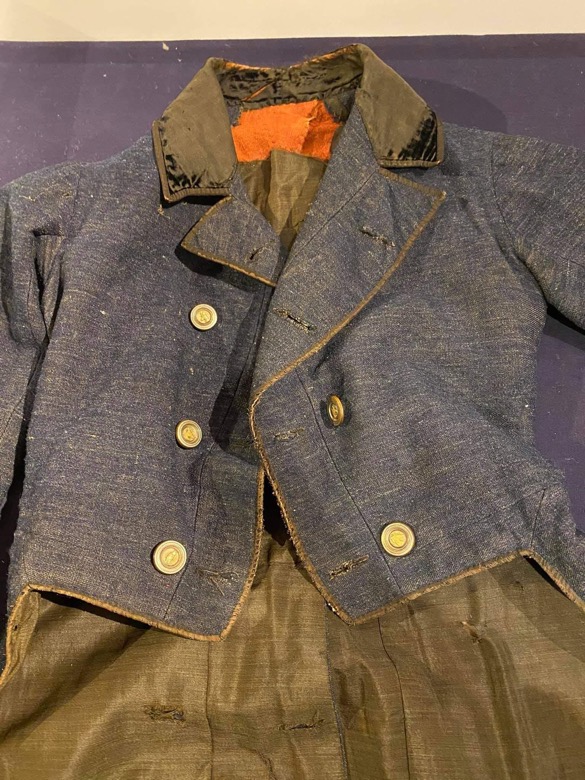

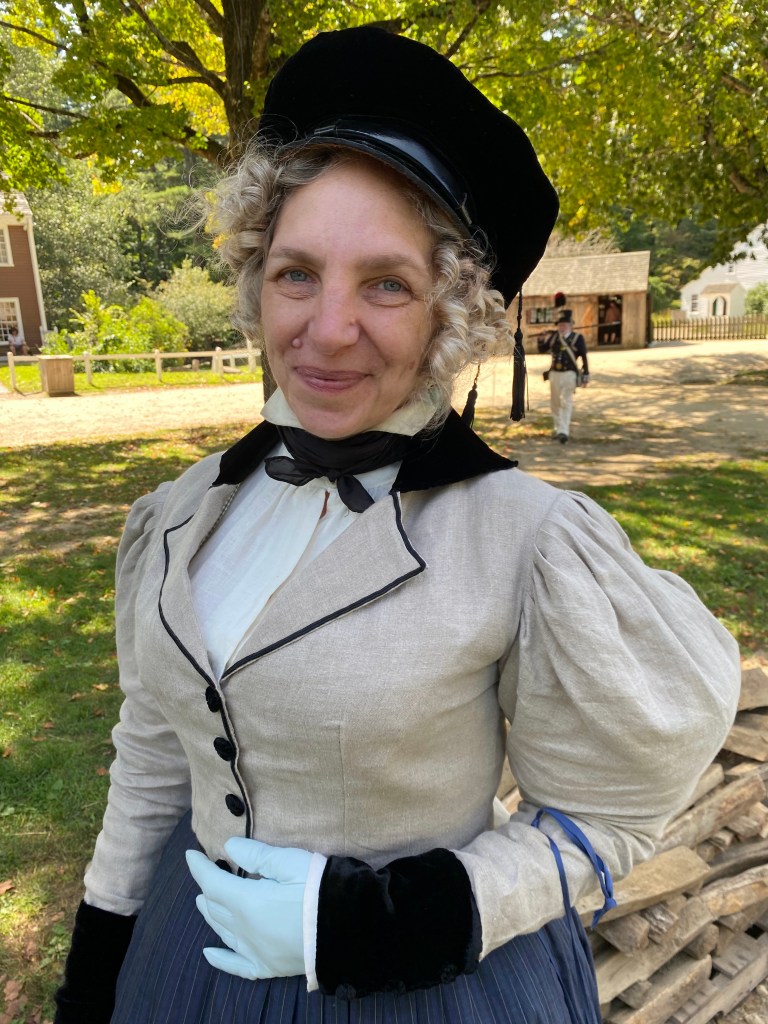
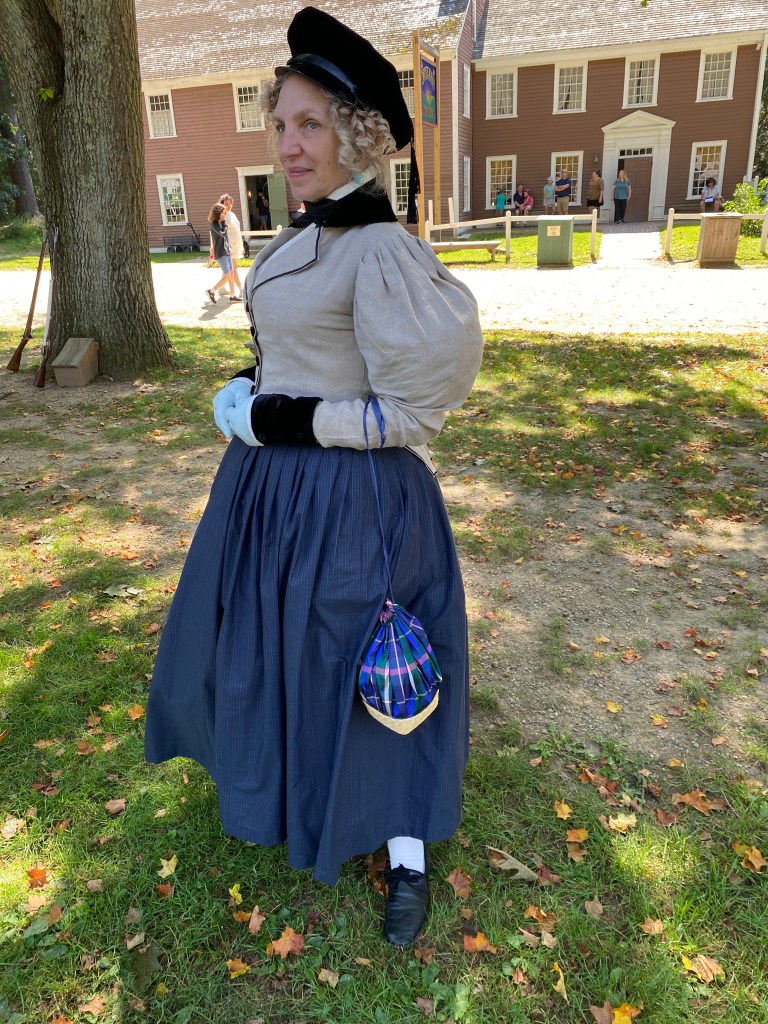
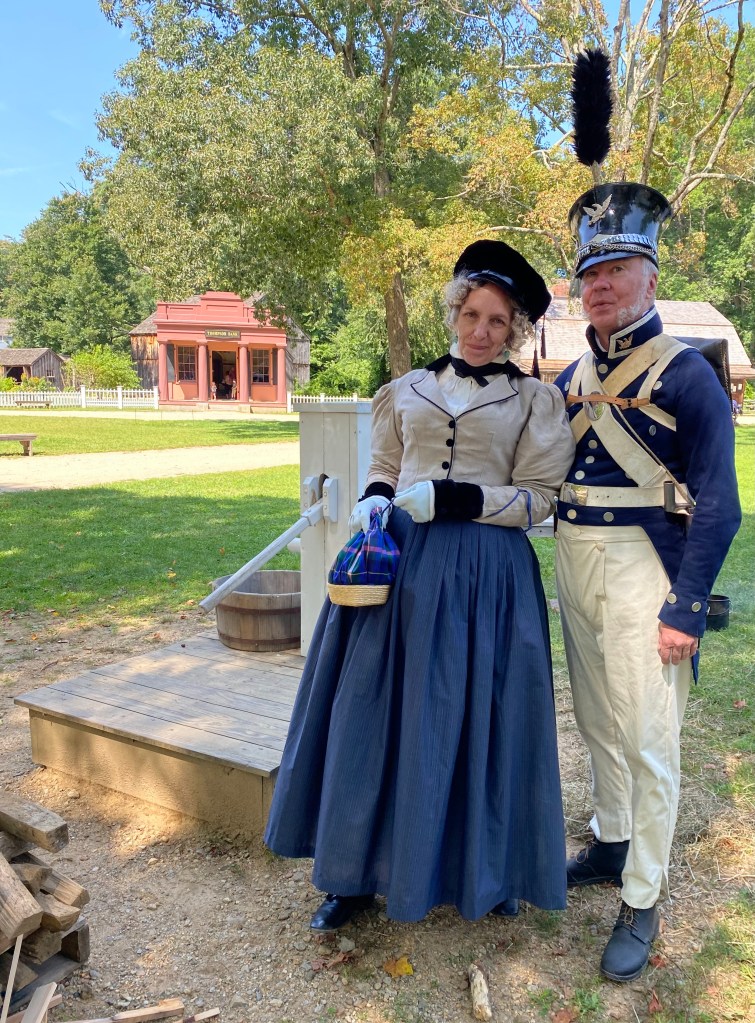
Reader, I began a dress in a workshop in May. I made another dress to wear and finished it the evening before the event. Why am I like this? (ADHD, I think.) Mr. K needed a new coat, so I patterned one for him to stitch from an older Burley & Trowbridge homespun. In 2021, someone (Genesee Country Village & Museum, maybe?) posted a fabulous image of a coat and waistcoat, which was the primary inspiration, along with coats including a blue broadcloth number at the DAR seen in the An Agreeable Tyrant exhibit. (Sadly, not in the online gallery.)

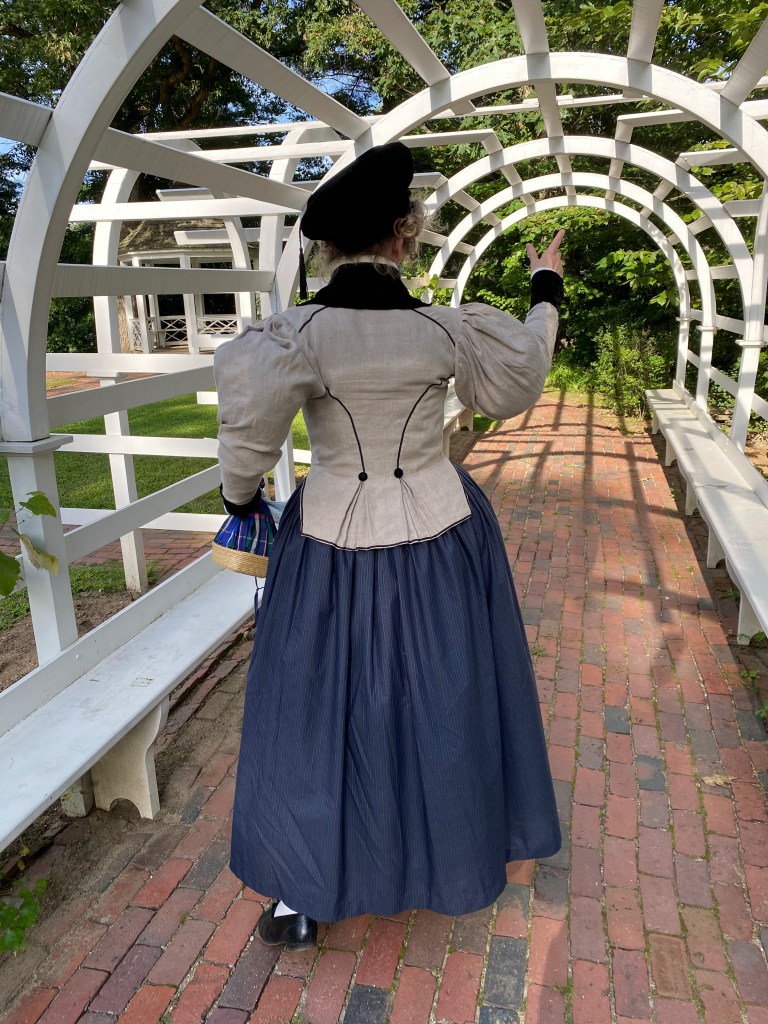
An Agreeable Tyrant also provided the inspiration for the dress I wore. I had almost too little sheer purple cotton fabric with a woven stripe, purchased at Lorraine Mill in Pawtucket a very long time ago. I meant to make an early 1800s gown, and had even started on the bodice around 2018 when life began to go very sideways and I stopped. I loved the fabric, though, and the deep color.
I started on Sunday, September 22, and finished on Sunday, October 6. I have a full-time job and am in graduate school, so I’m not entirely sure how I managed to do schoolwork, work-work, and gown-work but I’m pretty certain the One Weird Trick was to do no housework. It’s embarrassing when the cat’s fluffy tail picks up thread and lint, but it is a reliable measure of how much vacuuming is needed.
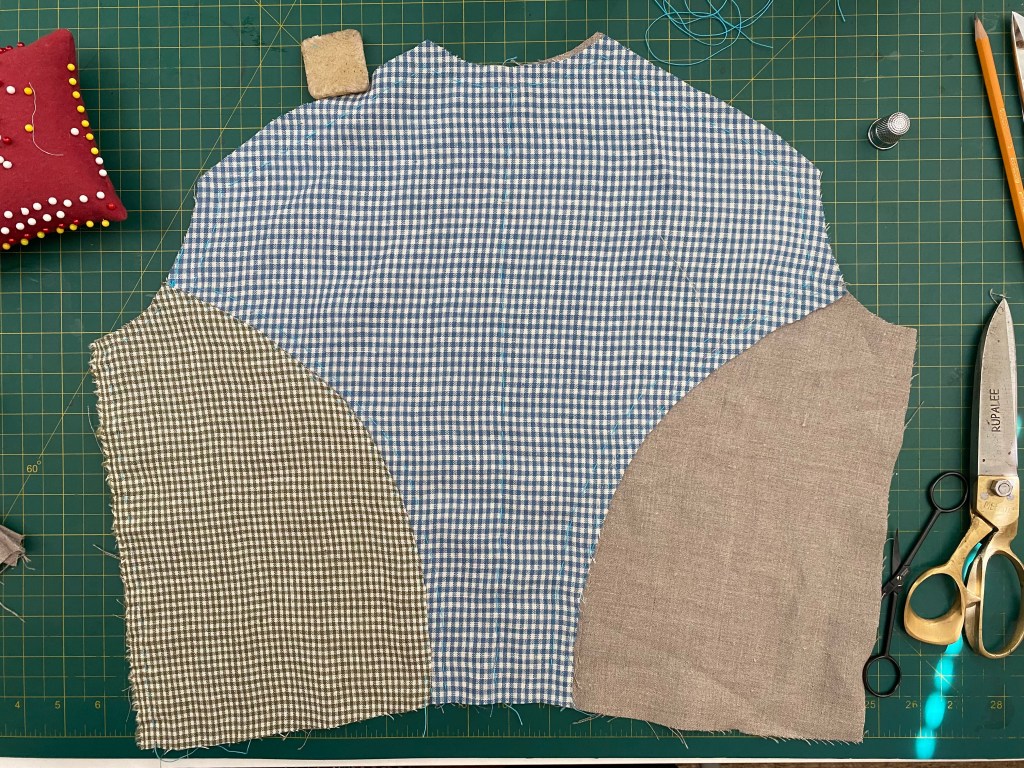
 The bodice closes in back with a drawstring, which is much the easiest method for me– I did not have time to fuss with the fittings buttons require. The front panel is a gathered rectangle with a band at the top, piped on both the top and bottom edges. A waistband joins the bodice and skirt. The sleeves and skirt were based on shapes I drafted in the Burnley & Trowbridge workshop (I swear I’ll finish that dress). The sleeve has a piped petal cap, which was a pain to make but very gothic, to go with the points that decorate the bodice neck edge, and of which I have no images. Since I had the space at B&T to draft the skirts full-size, they actually work now– astonishing– and make a satisfying conical shape. I’ve struggled with skirts since 2014, and it’s nice to have that solved after a decade!
The bodice closes in back with a drawstring, which is much the easiest method for me– I did not have time to fuss with the fittings buttons require. The front panel is a gathered rectangle with a band at the top, piped on both the top and bottom edges. A waistband joins the bodice and skirt. The sleeves and skirt were based on shapes I drafted in the Burnley & Trowbridge workshop (I swear I’ll finish that dress). The sleeve has a piped petal cap, which was a pain to make but very gothic, to go with the points that decorate the bodice neck edge, and of which I have no images. Since I had the space at B&T to draft the skirts full-size, they actually work now– astonishing– and make a satisfying conical shape. I’ve struggled with skirts since 2014, and it’s nice to have that solved after a decade!

I’ve started using Illustrator to figure out layouts when I am short on fabric. In this case, I only had a little more than 3 yards of fabric, but managed to get what I needed out of what I had. Sure, bigger sleeves would’ve been nice, but I managed long sleeves and that seems like an accomplishment.

Mr K. was able to debut his very apt and very dangerous velocipede, another project a decade in the making. We picked it up in February in Williamsburg. It is a handsome and impractical beast, tough to ride, but fun all the same. Charles Willson Peale and his sons had the first velocipede in the States, in Baltimore, so the Fort McHenry “1824” was truly appropriate. We entertained spectators, saw Mr. McC (who also took a turn about the site), and spent the day as very decorative appendages to the Museum’s tents. All in all, a day well spent.
























You must be logged in to post a comment.